Control and Protection Switch: 7 Powerful Benefits for Safer Electrical Systems

Outline for Control and Protection Switch
| Section | Details and LSI Keywords Covered |
|---|---|
| Introduction to Control and Protection Switch | electrical safety, switching devices |
| Control and Protection Switch Fundamentals | switch operation, power control |
| Importance of Control and Protection Switch | equipment safety, human protection |
| Historical Evolution of Control and Protection Switch | circuit protection history |
| Core Components of Control and Protection Switch | contacts, relays, housings |
| How a Control and Protection Switch Works | current flow, fault isolation |
| Control and Protection Switch in Industrial Systems | factories, automation |
| Control and Protection Switch in Residential Use | homes, distribution boards |
| Types of Control and Protection Switch | isolators, MCCB, ACB |
| Control and Protection Switch vs Circuit Breaker | comparison, advantages |
| Role of Control and Protection Switch in Automation | PLC integration |
| Safety Standards for Control and Protection Switch | IEC, ISO compliance |
| Control and Protection Switch Installation Practices | wiring, mounting |
| Common Faults in Control and Protection Switch | overheating, wear |
| Maintenance of Control and Protection Switch | inspections, testing |
| Energy Efficiency and Control and Protection Switch | power savings |
| Smart Control and Protection Switch Technology | IoT switches |
| Environmental Impact of Control and Protection Switch | sustainability |
| Selecting the Right Control and Protection Switch | ratings, application |
| Cost Considerations for Control and Protection Switch | budgeting |
| Control and Protection Switch in Renewable Energy | solar, wind |
| Troubleshooting Control and Protection Switch Issues | diagnostics |
| Future Trends in Control and Protection Switch | digital protection |
| FAQs about Control and Protection Switch | common questions |
| Conclusion on Control and Protection Switch | summary and outlook |
Introduction
The Control and Protection Switch stands at the heart of every safe electrical system. Whether in a factory humming with machines or a quiet residential building, this device silently manages power flow while guarding people and equipment. In simple terms, it controls electricity and protects circuits from damage. Yet, behind this simplicity lies a sophisticated balance of engineering, safety standards, and practical design.
In the first moments of any electrical fault, the Control and Protection Switch acts faster than human reflexes. It disconnects dangerous currents, limits damage, and restores stability. Therefore, its importance cannot be overstated. As electrical systems grow more complex, the role of this switch becomes even more vital.
Control and Protection Switch Fundamentals
A Control and Protection Switch combines two essential functions. First, it controls the flow of electrical energy. Second, it protects circuits from abnormal conditions. These abnormal conditions include overloads, short circuits, and ground faults.
Unlike a simple on-off switch, a Control and Protection Switch is engineered to react intelligently. It senses current levels and responds when limits are exceeded. Because of this dual role, it is widely used across industries. Moreover, it reduces the need for multiple separate devices, simplifying system design.
Importance of Control and Protection Switch
The importance of a Control and Protection Switch lies in safety and reliability. Electrical faults can cause fires, equipment failure, and serious injuries. However, with proper protection switching, risks are drastically reduced.
Additionally, these switches ensure uninterrupted operations. When faults are isolated quickly, unaffected areas continue working. As a result, downtime is minimized. In industries, this translates directly into cost savings and productivity gains.
Historical Evolution of Control and Protection Switch
In the early days of electricity, protection relied on fuses alone. While effective, fuses had limitations. They required replacement after every fault. Over time, engineers developed reusable protective switches.
The Control and Protection Switch evolved alongside industrial growth. Mechanical designs gave way to thermal and magnetic protection. Today, digital and smart versions dominate modern installations. Each step in this evolution improved safety and efficiency.
Core Components of Control and Protection Switch
A typical Control and Protection Switch includes contacts, a sensing mechanism, and an enclosure. The contacts open or close the circuit. The sensing mechanism detects abnormal conditions. The enclosure provides insulation and protection.
Some advanced designs include electronic sensors and communication modules. These components allow real-time monitoring. Therefore, operators gain better visibility and control over electrical systems.
How a Control and Protection Switch Works
The working principle is straightforward yet powerful. Under normal conditions, current flows freely. When a fault occurs, the sensing mechanism detects excess current. Immediately, the switch opens the circuit.
This rapid action prevents damage. Furthermore, many switches allow manual or automatic reset. This feature reduces maintenance time and improves system uptime.
Control and Protection Switch in Industrial Systems
In industrial environments, electrical loads are heavy and continuous. Motors, conveyors, and automation equipment rely on stable power. A Control and Protection Switch ensures each load operates safely.
Moreover, industries often use coordinated protection. This means switches are set to operate in sequence. Consequently, only the faulty section shuts down, while the rest continues running.
Control and Protection Switch in Residential Use
In homes, the Control and Protection Switch plays a quieter role. It protects appliances, wiring, and occupants. From air conditioners to kitchen equipment, every circuit benefits from proper switching and protection.
Modern homes increasingly use compact and smart switches. These designs fit neatly into distribution boards and enhance safety without complexity.
Types of Control and Protection Switch
There are several types, each designed for specific applications. Common examples include isolator switches, molded case circuit breakers, and air circuit breakers. Each type offers different current ratings and protection levels.
Choosing the right type depends on load size and environment. Therefore, understanding application requirements is essential.
Control and Protection Switch vs Circuit Breaker
Although similar, a Control and Protection Switch often integrates control features not found in basic breakers. Circuit breakers focus mainly on protection. Control switches add operational flexibility.
As a result, combined devices reduce component count. This simplification lowers installation and maintenance costs.
Role of Control and Protection Switch in Automation
Automation systems depend on precise control. A Control and Protection Switch integrates seamlessly with PLCs and control panels. It allows remote operation and fault reporting.
This integration improves response time. Consequently, operators can address issues before they escalate.
Safety Standards for Control and Protection Switch
Safety standards guide the design and application of these switches. International standards ensure reliability and compatibility. Compliance guarantees predictable performance under fault conditions.
Adhering to standards also simplifies inspections. Therefore, it builds trust among engineers and regulators alike.
Control and Protection Switch Installation Practices
Proper installation is crucial. Incorrect wiring or mounting can reduce effectiveness. Installers must follow manufacturer guidelines and local codes.
Clear labeling and accessibility further enhance safety. These practices ensure quick response during emergencies.
Common Faults in Control and Protection Switch
Over time, switches may experience wear. Common faults include contact erosion and overheating. Environmental factors like dust and moisture can worsen these issues.
Regular inspections help detect early signs of failure. Thus, preventive action avoids unexpected breakdowns.
Maintenance of Control and Protection Switch
Maintenance keeps systems reliable. Routine checks include tightening connections and testing trip mechanisms. Cleaning also prevents insulation breakdown.
Scheduled maintenance extends service life. Moreover, it ensures consistent performance.
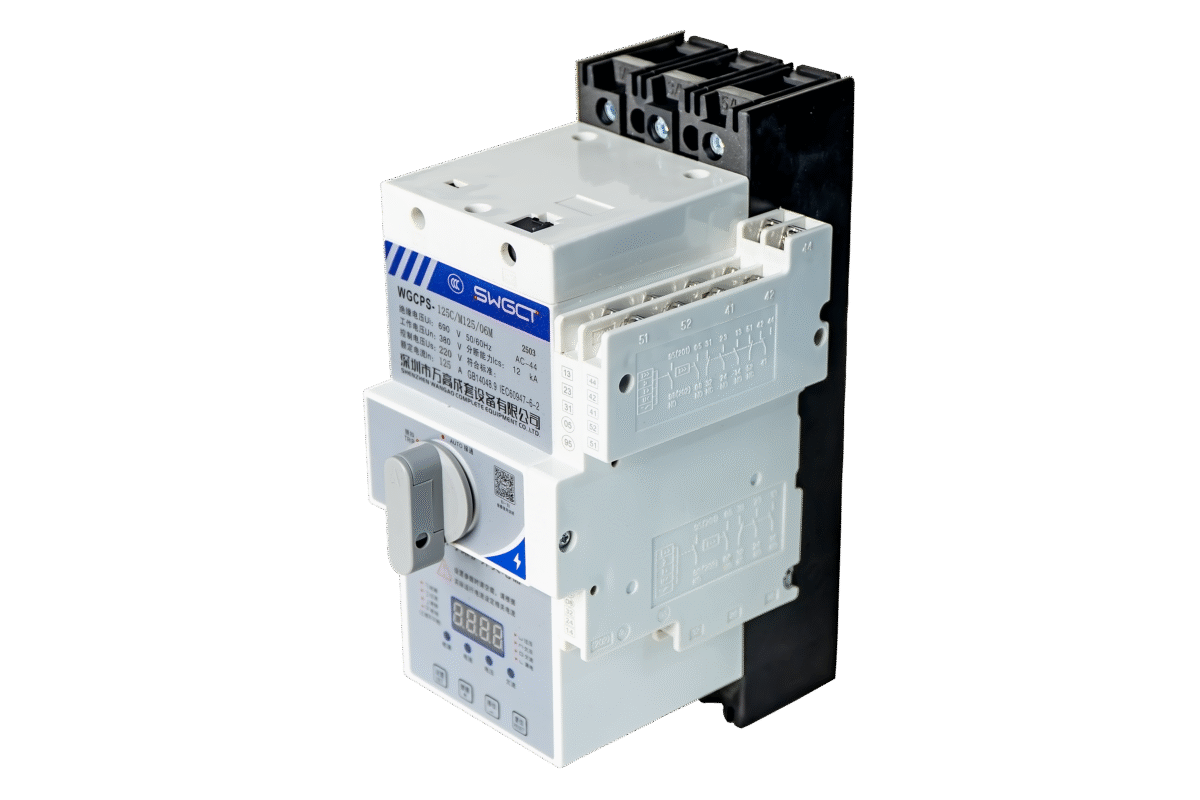
Energy Efficiency and Control and Protection Switch
Efficient switching reduces energy losses. Modern designs minimize resistance and heat generation. As a result, overall system efficiency improves.
Energy savings may seem small individually. However, across large systems, they add up significantly.
Smart Control and Protection Switch Technology
Smart switches represent the future. They feature sensors, communication, and analytics. Operators receive alerts and performance data in real time.
This intelligence supports predictive maintenance. Therefore, failures are prevented rather than merely managed.
Environmental Impact of Control and Protection Switch
Sustainable design matters. Manufacturers now use recyclable materials and energy-efficient production. Longer product life reduces waste.
Environmentally friendly switches support green building goals. Thus, they align with global sustainability efforts.
Selecting the Right Control and Protection Switch
Selection depends on current rating, voltage, and environment. Incorrect selection leads to poor performance. Consulting technical specifications is essential.
A well-chosen switch enhances safety and reliability. Hence, it is an investment, not a cost.
Cost Considerations for Control and Protection Switch
Initial cost varies by type and features. However, long-term savings often outweigh upfront expenses. Reduced downtime and maintenance lower overall costs.
Therefore, value matters more than price alone.
Control and Protection Switch in Renewable Energy
Renewable systems face unique challenges. Variable power and environmental exposure demand robust protection. Control and Protection Switch devices ensure safe operation of solar and wind installations.
They also support grid integration. This role is increasingly important as renewable energy expands.
Troubleshooting Control and Protection Switch Issues
When issues arise, systematic troubleshooting helps. Checking load conditions and wiring often reveals problems. Diagnostic indicators simplify the process.
Quick resolution minimizes disruption. Hence, troubleshooting skills are valuable.
Future Trends in Control and Protection Switch
The future points toward digitalization. Smart grids and connected devices demand advanced switching solutions. Control and Protection Switch technology will continue evolving.
Innovation will focus on safety, efficiency, and intelligence. The journey is far from over.
FAQs
What is a Control and Protection Switch used for?
It controls electrical circuits and protects them from faults.
Is a Control and Protection Switch necessary in homes?
Yes, it enhances safety and protects appliances.
How often should a Control and Protection Switch be maintained?
Regular inspection is recommended at least annually.
Can a Control and Protection Switch replace a fuse?
In many cases, yes, offering reusable protection.
Are smart Control and Protection Switch devices reliable?
Yes, they add monitoring and predictive features.
What industries use Control and Protection Switch systems most?
Manufacturing, energy, and infrastructure sectors rely heavily on them.
Conclusion
The Control and Protection Switch is a cornerstone of electrical safety. It balances control and protection in a single, reliable device. From homes to heavy industries, its role is universal and indispensable.
As technology advances, these switches become smarter and more efficient. Investing in the right Control and Protection Switch ensures safety, reliability, and peace of mind for years to come.


