High-Speed Automatic Transfer Switch: 8 Mission-Critical Benefits for Dual Power Supply in Data Center Rack PDU
Outline for High-Speed Automatic Transfer Switch for Dual Power Supply in Data Center Rack PDU
| Section | Details and LSI Keywords Covered |
|---|---|
| Introduction to High-Speed Automatic Transfer Switch for Rack PDU | data center power continuity |
| Understanding High-Speed Automatic Transfer Switch Technology | fast transfer ATS |
| Why Dual Power Supply Is Essential in Data Center Rack PDU | redundancy |
| Evolution of Automatic Transfer Switching in Data Centers | critical power |
| Core Components of High-Speed ATS for Rack PDU | relays, controller |
| Transfer Speed and Its Importance in IT Loads | milliseconds switching |
| How High-Speed ATS Works in a Rack PDU | automatic changeover |
| Integration with Data Center Power Architecture | UPS, PDU |
| Single-Cord vs Dual-Cord Load Protection | IT equipment safety |
| Electrical Ratings and Load Capacity Considerations | current limits |
| Safety and Interlocking Mechanisms | source isolation |
| Zero-Crossing and Break-Before-Make Operation | power quality |
| Impact on Server Uptime and Availability | SLA protection |
| Installation in Rack-Level PDU Systems | compact design |
| Monitoring and Status Indication | LEDs, alarms |
| Communication and Remote Monitoring Options | SNMP, Modbus |
| Compatibility with UPS and Power Feeds | A/B power |
| Thermal Management and Efficiency | low losses |
| Compliance with Data Center Standards | IEC, UL, TIA |
| Maintenance and Testing Procedures | periodic checks |
| Common Failure Scenarios and Mitigation | fault tolerance |
| Applications in Enterprise Data Centers | IT racks |
| Applications in Edge and Micro Data Centers | compact facilities |
| Role in High-Availability Tier III and IV Designs | redundancy |
| Selecting the Right High-Speed ATS for Rack PDU | selection guide |
| Cost, Risk Reduction, and Lifecycle Value | ROI |
| Future Trends in Rack-Level Power Transfer | intelligent PDU |
| FAQs about High-Speed Automatic Transfer Switch | common questions |
| Conclusion on High-Speed Automatic Transfer Switch for Rack PDU | summary |
Introduction
A High-speed automatic transfer switch for dual power supply in data center rack PDU is a critical component in modern IT infrastructure. Data centers depend on continuous power availability to maintain server uptime, protect data integrity, and meet strict service-level agreements. Even a momentary power interruption at the rack level can result in server crashes, data loss, and operational disruption.
To address this risk, high-speed automatic transfer switches are integrated directly into rack PDUs. These devices ensure instantaneous switching between two independent power sources, typically referred to as A and B feeds. Their speed, reliability, and compact design make them indispensable in high-availability data center environments.
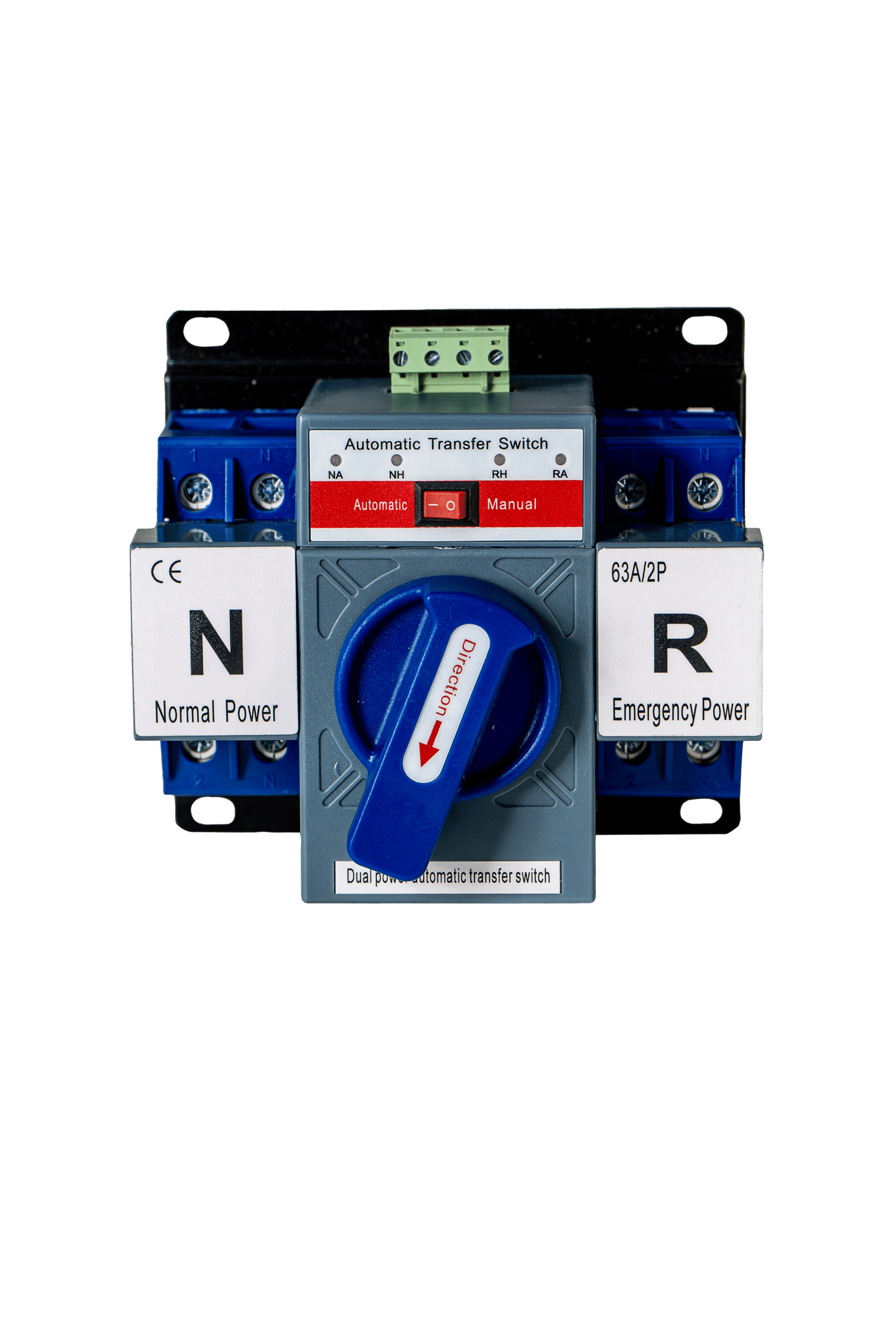
Understanding High-Speed Automatic Transfer Switch Technology
A high-speed automatic transfer switch is designed to transfer loads between two power sources within milliseconds. Unlike conventional ATS devices used at facility level, rack-level high-speed ATS units prioritize speed and precision.
They are engineered specifically for sensitive IT loads that cannot tolerate power interruption. This makes them ideal for servers, storage systems, and network equipment housed within data center racks.
Why Dual Power Supply Is Essential in Data Center Rack PDU
Dual power supply architecture is a foundational principle of data center design. Each rack is typically fed by two independent power sources to eliminate single points of failure.
A rack PDU equipped with a high-speed ATS ensures that if one source fails, the second source takes over instantly. This redundancy protects IT equipment and supports uninterrupted operation.
Evolution of Automatic Transfer Switching in Data Centers
Early data centers relied on dual-corded equipment and manual switching. As power densities increased, this approach became insufficient.
The evolution toward high-speed automatic transfer switches reflects the need for faster, smarter, and more reliable power transfer at the rack level. Modern ATS designs are optimized for IT environments and high-density racks.
Core Components of High-Speed ATS for Rack PDU
Key components include fast-acting relays or solid-state switching elements, a control processor, and voltage sensing circuits. These components work together to detect power anomalies instantly.
The control logic determines the healthiest power source and initiates transfer without delay. High-quality components ensure consistent performance under continuous operation.
Transfer Speed and Its Importance in IT Loads
IT equipment is extremely sensitive to power interruptions. Even a brief outage of a few milliseconds can cause servers to reboot.
High-speed ATS units are designed to switch within a time window that IT power supplies can ride through. This speed ensures uninterrupted operation and protects critical workloads.
How High-Speed ATS Works in a Rack PDU
Under normal conditions, the ATS connects the rack load to the preferred power source. It continuously monitors voltage and frequency on both feeds.
When a disturbance is detected, the ATS disconnects the failing source and connects the alternate source almost instantaneously. Once stability is restored, it can revert automatically or remain latched based on configuration.
Integration with Data Center Power Architecture
Rack-level ATS devices integrate seamlessly with UPS systems, power distribution units, and upstream switchgear. They act as the final layer of redundancy before IT equipment.
This integration supports end-to-end power resilience. It ensures that redundancy designed at facility level is preserved at the rack level.
Single-Cord vs Dual-Cord Load Protection
Many IT devices are single-corded. Without a rack ATS, these devices cannot benefit from dual power feeds.
A high-speed ATS enables single-corded equipment to achieve dual-source redundancy. This capability expands flexibility in equipment selection and rack design.
Electrical Ratings and Load Capacity Considerations
Rack ATS units are rated for specific current and voltage levels. Common ratings support typical rack loads and branch circuits.
Proper sizing ensures reliable operation and prevents overheating. Load assessment is essential when selecting the right ATS.
Safety and Interlocking Mechanisms
Safety is critical in rack-level power systems. High-speed ATS devices include electrical interlocks to prevent simultaneous connection of both sources.
This break-before-make operation prevents backfeeding and protects upstream equipment. It ensures safe and controlled power transfer.

Zero-Crossing and Break-Before-Make Operation
Advanced ATS designs use zero-crossing switching to minimize electrical stress. This technique reduces transients during transfer.
Break-before-make logic ensures complete isolation between sources. Together, these features protect sensitive IT equipment.
Impact on Server Uptime and Availability
High-speed automatic transfer switches directly support uptime objectives. By preventing power interruptions, they help maintain continuous server operation.
This reliability is essential for meeting service-level agreements. It also protects business continuity and customer trust.
Installation in Rack-Level PDU Systems
Rack ATS units are designed for compact installation within PDUs or as inline devices. Their form factor fits standard rack environments.
Installation is straightforward when performed by qualified technicians. Clear labeling and cable management enhance safety.
Monitoring and Status Indication
Visual indicators show power source status and transfer events. These indicators provide immediate feedback to operators.
Clear status information simplifies troubleshooting. It also supports proactive power management.
Communication and Remote Monitoring Options
Some high-speed ATS models support communication protocols. These interfaces allow integration with data center monitoring systems.
Remote monitoring enhances visibility. Operators can track power events and plan maintenance effectively.
Compatibility with UPS and Power Feeds
Rack ATS units are compatible with UPS-protected power feeds. They support A/B feed architectures commonly used in data centers.
This compatibility ensures seamless coordination with upstream power systems.
Thermal Management and Efficiency
Efficient switching elements minimize power loss and heat generation. Thermal performance is critical in high-density racks.
Low losses improve energy efficiency and reduce cooling requirements.
Compliance with Data Center Standards
High-speed ATS devices comply with IEC, UL, and data center design standards. Compliance ensures safety and interoperability.
Certified equipment simplifies audits and regulatory approval.
Maintenance and Testing Procedures
Maintenance requirements are minimal. Periodic functional testing ensures readiness.
Regular inspection of connections and indicators supports long-term reliability.
Common Failure Scenarios and Mitigation
Potential issues include source instability or control faults. Redundant monitoring helps detect problems early.
Proper design and quality components mitigate failure risks.
Applications in Enterprise Data Centers
Enterprise data centers rely on rack ATS devices to protect mission-critical workloads. These switches support high-density and mixed-load racks.
Their reliability supports enterprise IT operations.
Applications in Edge and Micro Data Centers
Edge and micro data centers often use compact racks. High-speed ATS units fit these environments perfectly.
They provide enterprise-level redundancy in smaller facilities.
Role in High-Availability Tier III and IV Designs
High-availability data centers require redundancy at every level. Rack-level ATS devices support Tier III and Tier IV architectures.
They eliminate single points of failure at the rack level.
Selecting the Right High-Speed ATS for Rack PDU
Selection depends on transfer speed, load rating, and compatibility. Monitoring features and form factor are also important.
Expert selection ensures optimal performance and reliability.
Cost, Risk Reduction, and Lifecycle Value
While rack ATS units add cost, they significantly reduce risk. Preventing downtime delivers substantial financial value.
Lifecycle benefits far exceed initial investment.
Future Trends in Rack-Level Power Transfer
Future designs will integrate intelligent analytics and predictive diagnostics. Rack ATS units will become smarter and more connected.
These advancements will further enhance data center resilience.
Preguntas frecuentes
What is a high-speed automatic transfer switch for rack PDU?
It is a device that instantly switches between two power sources at the rack level.
Why is high-speed transfer important?
It prevents server downtime caused by brief power interruptions.
Can it protect single-corded equipment?
Yes, it enables redundancy for single-cord loads.
Is it compatible with UPS systems?
Yes, it is designed to work with UPS-fed power sources.
Does it require frequent maintenance?
No, minimal periodic testing is sufficient.
Is it necessary for all data centers?
It is essential for high-availability environments.
Conclusion
The High-speed automatic transfer switch for dual power supply in data center rack PDU is a vital safeguard for modern IT infrastructure. By providing instantaneous power transfer at the rack level, it eliminates one of the most critical risks in data center operation.
As data centers continue to evolve toward higher density and availability, rack-level high-speed ATS solutions will remain essential. Investing in this technology ensures uptime, protects critical equipment, and supports long-term operational resilience.


